PANCHAMKARMA THERAPIES
Ayurveda defines health as a condition where the body is clear of toxins and organs are functioning normally, the mind is peace and emotions are clam and happy in a stressful and toxic environment. Our physical and mental system accumulates toxins causing deterioration in functioning of body mind complex which opens the door for chronic, degenerative and nonspecific diseases to develop.
Purvakarma: Pre-purification Measures
Benefits Of Panchakarma:
- Helps Restore Metabolic Fire (Agni)
- Eliminates ama (Toxins) Strengthens Tissue
- Functions
- Slows the Aging Process
- Balance all Three Doshas
- Reduces Stress Improves Relaxation & Tolerance
- Detoxification of Body & Mind
Five Basic Shodanas: Cleansing Methods:




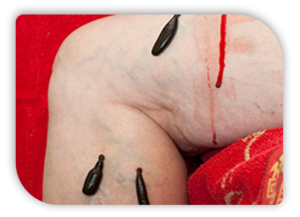
Rakta moksha is also indicated for cases of enlarged liver, spleen and gout. Pitta is produced from the disintegrated red blood cells in the liver. So pitta and blood have a very close relationship. An increase in pitta may go into the blood causing toxicity, and thus many pitta genic disorders. Extracting a small amount of blood from a vein relieves the tension created by the pittagenic toxins in the blood. Bloodletting also stimulates the spleen to produce anti-toxic substances that help to stimulate the immune system. Toxins are neutralized, enabling radical cures in many bloodborne disorders.
Certain substances such as sugar, salt, yogurt, sour tasting foods and alcohol are toxic to the blood. In certain blood disorders these substances should be avoided to keep the blood pure. For raktamoksha treatment other than bloodletting, there are blood-purifying practices involving herbs, gem therapy or color water therapy. For any rakta moksha treatment or related alternative treatment, it is beneficial to refrain from yogurt, salt, sugar, alcohol, marijuana, sour and fermented foods.
